| Dose-response parameters and microdosimetric quantity [3] |
| Neutrons |
| Neutrons | |||||||||||
| Laboratory | Source | Reference | Types of | Mean energy | Linear term (Dics/cell/Gy)** | Quadratic term (Dics/cell/Gy2)** | Maximum RBE*** | ||||
| neutrons | E (MeV) | α/Gy | ± | S.E. | Fixed at β=k=5.355×10-2 | RBEm | ± | S.E. | |||
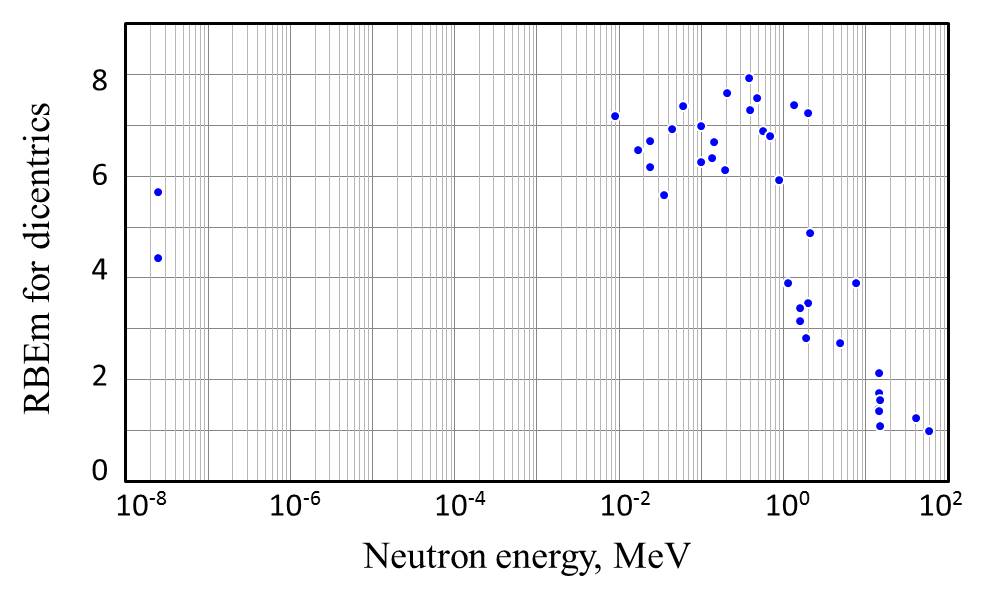
| 1 | HU-T(d,n)He | K1 | Monoenergetic | 14.1 | 0.229 | ± | 0.020 | 5.355×10-2 | 14.136 | ± | 1.235 |
| 1 | NIRS-Be(d,n)B | K1, K2 | Monoenergetic | 2.03 | 0.566 | ± | 0.094 | 5.355×10-2 | 34.938 | ± | 5.802 |
| 1 | KUR-Nth | K2 | Thermal | 2.50E-08 | 0.920 | ± | 0.028 | 5.355×10-2 | 56.815 | ± | 1.747 |
| 1 | TKY-GH | K3, K4 | Fission | 1.354 | 1.197 | ± | 0.023 | 5.355×10-2 | 73.889 | ± | 1.432 |
| 1 | TKY-TC | K3, K4 | Fission | 0.477 | 1.219 | ± | 0.024 | 5.355×10-2 | 75.235 | ± | 1.506 |
| 1 | TKY-MD | K3, K4 | Fission | 0.009 | 1.164 | ± | 0.045 | 5.355×10-2 | 71.852 | ± | 2.778 |
| 1 | TKY-BL | K3 | Fission (filtered) | 0.21 | 1.237 | ± | 0.033 | 5.355×10-2 | 76.358 | ± | 2.006 |
| 1 | TKY-M12 | K3 | Fission (filtered) | 0.045 | 1.123 | ± | 0.039 | 5.355×10-2 | 69.296 | ± | 2.380 |
| 1 | TKY-M27 | K3 | Fission (filtered) | 0.017 | 1.056 | ± | 0.019 | 5.355×10-2 | 65.165 | ± | 1.186 |
| 1 | KUR-U | K4 | Fission | 1.985 | 1.172 | ± | 0.070 | 5.355×10-2 | 72.315 | ± | 4.314 |
| 1 | KUR-B1 | K3 | Fission (filtered) | 0.06 | 1.195 | ± | 0.019 | 5.355×10-2 | 73.740 | ± | 1.186 |
| 1 | UTR-Air | K3, K4 | Fission | 0.101 | 1.132 | ± | 0.044 | 5.355×10-2 | 69.888 | ± | 2.723 |
| 1 | UTR-Bi | K3 | Fission (filtered) | 0.138 | 1.028 | ± | 0.084 | 5.355×10-2 | 63.467 | ± | 5.214 |
| 1 | UTR-Fe | K3, K4 | Fission (filtered) | 0.196 | 0.992 | ± | 0.038 | 5.355×10-2 | 61.239 | ± | 2.374 |
| 1 | UTR-PE | K3, K4 | Fission (filtered) | 0.1 | 1.015 | ± | 0.078 | 5.355×10-2 | 62.644 | ± | 4.845 |
| 2 | GSF-QM | G1, G8 | Quasimonoenergetic | 0.144 | 0.786 | ± | 0.066 | 5.355×10-2 | 66.610 | ± | 5.593 |
| 2 | GSF-QM | G2, G8 | Quasimonoenergetic | 0.565 | 0.813 | ± | 0.052 | 5.355×10-2 | 68.898 | ± | 4.407 |
| 2 | T(d,n) | G3 | Monoenergetic | 14.5 | 0.204 | ± | 0.017 | 5.355×10-2 | 17.288 | ± | 1.441 |
| 2 | T(d,n) | G4 | Monoenergetic | 15.0 | 0.127 | ± | 0.025 | 5.355×10-2 | 10.763 | ± | 2.119 |
| 2 | Nth | G5 | Thermal | 2.50E-08 | 0.517 | ± | 0.023 | 5.355×10-2 | 43.814 | ± | 1.949 |
| 2 | Q-M | G6 | Quasimonoenergetic | 41 | 0.146 | ± | 0.016 | 5.355×10-2 | 12.373 | ± | 1.356 |
| 2 | Q-M | G6 | Quasimonoenergetic | 60 | 0.115 | ± | 0.026 | 5.355×10-2 | 9.746 | ± | 2.203 |
| 2 | MEDAPP | G7 | Monoenergetic | 1.9 | 0.332 | ± | 0.020 | 5.355×10-2 | 28.136 | ± | 1.695 |
| 2 | 7Li(p,n)7Be | G8 | Monoenergetic | 0.036 | 0.664 | ± | 0.098 | 5.355×10-2 | 56.271 | ± | 8.305 |
| 2 | 7Li(p,n)7Be | G8 | Monoenergetic | 0.385 | 0.935 | ± | 0.073 | 5.355×10-2 | 79.237 | ± | 6.186 |
| 2 | T(p,n)3He | G8 | Monoenergetic | 1.151 | 0.458 | ± | 0.041 | 5.355×10-2 | 38.814 | ± | 3.475 |
| 2 | D(d,n)3He | G8 | Monoenergetic | 4.85 | 0.320 | ± | 0.024 | 5.355×10-2 | 27.119 | ± | 2.034 |
| 2 | T(d,n)4He | G8 | Monoenergetic | 14.6 | 0.162 | ± | 0.015 | 5.355×10-2 | 13.729 | ± | 1.271 |
| 2 | Fission | G9, G8 | Fission | 1.6 | 0.400 | ± | 0.020 | 5.355×10-2 | 33.898 | ± | 1.695 |
| 2 | Fission | G10, G8 | Fission | 1.6 | 0.370 | ± | 0.020 | 5.355×10-2 | 31.356 | ± | 1.695 |
| 3 | Filtered | H1, H2 | Filtered fission | 0.024 | 0.821 | ± | 0.031 | 5.355×10-2 | 66.802 | ± | 2.522 |
| 3 | Filtered | H3 | Filtered fission | 0.024 | 0.872 | ± | 0.032 | 5.355×10-2 | 70.952 | ± | 2.604 |
| 3 | Fission | H4 | Fission | 0.7 | 0.835 | ± | 0.010 | 5.355×10-2 | 67.933 | ± | 0.838 |
| 3 | Fission | H4 | Fission | 0.9 | 0.728 | ± | 0.024 | 5.355×10-2 | 59.211 | ± | 1.912 |
| 3 | Be(d,n) | H-4 | Monoenergetic | 7.6 | 0.478 | ± | 0.033 | 5.355×10-2 | 38.885 | ± | 2.718 |
| 3 | T(d,n) | H-4 | Monoenergetic | 14.7 | 0.262 | ± | 0.040 | 5.355×10-2 | 21.286 | ± | 3.222 |
| 3 | 252Cf | H-5 | Fission | 2.13 | 0.600 | ± | 0.010 | 5.355×10-2 | 48.820 | ± | 0.814 |
| 3 | T(d,n) | H-6 | Monoenergetic | 14.9 | 0.195 | ± | 0.018 | 5.355×10-2 | 15.867 | ± | 1.465 |
| 3 | Fe filtered | H-1 | Filtered fission | 0.024 | 0.759 | ± | 0.026 | 5.355×10-2 | 61.758 | ± | 2.116 |
| 4 | Fission | O-2 | Fission | 0.4 | 0.896 | ± | 0.069 | 5.355×10-2 | 75.932 | ± | 5.847 |
| 4 | Fission | O-1 | Fission | 0.21 | 1.216 | ± | 0.092 | 5.355×10-2 | 75.062 | ± | 5.660 |
| 4 | d(16)+Be | O-3 | Quasimonoenergetic | 6.5 | 0.416 | ± | 0.038 | 5.355×10-2 | 16.378 | ± | 1.476 |
| 4 | d(33)+Be | O-3 | Quasimonoenergetic | 14 | 0.184 | ± | 0.092 | 5.355×10-2 | 7.232 | ± | 3.638 |
| 4 | d(50)+Be | O-3 | Quasimonoenergetic | 21 | 0.139 | ± | 0.024 | 5.355×10-2 | 5.472 | ± | 0.961 |
| *) [1]: RBC, Kyoto University, Japan (K). [2]: GSF, Munchen, Germany (G). [3]: NRPB, Harwell, UK (H). [4]: Other laboratories (O) | |||||||||||
| **) Dose-response of dicentrics was fitted to Y=(αg+βgDg)Dg+(αn+βnDn)Dn, βg=βn=k=5.355×10-2/Gy2. Subscript (g) denotes γ-rays and (n) denotes neutrons. Parameters were obtained by iteratively reweighted ML method. | |||||||||||
| ***) Maximum RBE, RBEm=αn/αg. The linear term (αg) for reference radiation (60Co γ-rays) was obtained for the laboratory pooled data. | |||||||||||
| It was 0.0162/cell/Gy for RBC, 0.0118/cell/Gy for GSF and 0.0123/cell/Gy for NRPB. That of other laboratories was author dependent, where head-to-head experiment is performed for reference radiation. | |||||||||||

References
(K1) Sasaki, M. S. (1971): Radiation-induced
chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes: possible biological dosimeter
in man. In; Sugahara, T. and Hag, O. eds., Biological Aspects of Radiation
Protection. Tokyo, Igaku Shoin Ltd., Berlin, Springer, pp.81-91.
(K2) Sasaki, M.
S., Endo, S., Ejima, Y., et al. (2006): Effective dose of A-bomb radiation in
Hiroshima and Nagasaki as assessed by chromosomal effectiveness of spectrum
energy photons and neutrons. Radiat. Environ. Biophys., 45:79-91.
(K3) Sasaki, M. S.,
Nomura, T., Ejima, Y., et al. (2008): Experimental derivation of relative
biological effectiveness of A-bomb neutrons in Hiroshima and Nagasaki and
implication for risk assessment. Radiat. Res., 170:101-117.
(K4) Sasaki, M. S., Saigusa, S., Kimura,
I., Kobayashi, T., Ikushima, T., Kobayashi, K., Saito, I., Sasuga, N.,
Oka, Y., Ito, T. and Kondo, S. (1992): Biological effectiveness of fission
neutrons: energy dependency and its implication for the risk assessment.
Proceedings of the International Conference on Radiation Effects and Protection,
Ibaraki, pp. 31-35.
(G1) Schmid, E.,
Regulla, D., Guldbakke, S., Schlegel, D. and Roos, M. (2002): Relative
biological effectiveness of 144 keV neutrons in producing dicentric chromosomes
in human lymphocytes compared with 60Co gamma rays under
head-to-head conditions. Radiat. Res., 157, 453-460.
(G2) Schmid, E., Regulla, D., Guldbakke,
S., Schlegel, D. and Bauchinger, M. (2000): The effectiveness of monoenergetic
neutrons at 565 keV in producing dicentric chromosomes in human lymphocytes
at low doses. Radiat. Res., 154, 307-312.
(G3) Bauchinger, M., Kuhm, H., Dresp, J.
et al. (1983): Doseeffect relationship for 14.5 MeV (d+T) neutron-induced
chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes irradiated in a man phantom.
Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 43:571-578.
(G4) Bauchinger,
M., Schmid, E., Rimpl, G., et al. (1975): Chromosome aberrations induced in
human lymphocytes after irradiation with 15.0 MeV neutrons in vitro. I. Dose-response relation and RBE. Mutation Res.,
27:103-109.
(G5) Schmid, T. E., Oestreicher, U., Molls,
M. and Schmid, E. (2013): RBE of thermal neutrons for induction of chromosome
aberrations in human lymphocytes. Radiat. Environ. Biophys., 52:113-121.
(G6) Nolte, R.,
Muhbrade, K-H., Meulders, J. P., et al. (2005): RBE of quasi-nomoenergetic 60
MeV neutron radiation for induction of dicentric chromosomes in human
lymphocytes. Radiat. Environ. Biophys., 44:201-209.
(G7) Schmid, E.,
Wagner, F. M., Romm, H. et al. (2009): Dose-response relationship of dicentric
chromosomes in human lymphocytes obtained for the fission neutron therapy
facility MEAPP at the research reactor FRM II. Radiat. Environ. Biophys.,
48:67-75.
(G8) Schmid, E., Schlegel, D., Guldbackke,
S., Kapsch, R. –P. and Regulla, D. (2003): RBE of nearly monoenergetic
neutrons at energies of 36 keV-14.6 MeV for induction of dicentrics in
human lymphocytes. Radiat. Environ. Biophys., 42, 87-94.
(G9) Bauchinger,
M., Koester, L., Schmid, E., Dresp, J. and Streng, S. (1984): Chromosome
aberrations in human lymphocytes induced by fission neutrons. Int. J. Radiat.
Biol., 45, 449-457.
(G10) Schmid, E., Schraube, H. and Bauchinger,
M. (1998): Chromosome aberration frequencies in human lymphocytes irradiated
in a phantom by a mixed beam of fission neutrons and γ-rays. Int. J. Radiat.
Biol., 73:263-267.
(H1) Lloyd, D. C., Edwards, A. A., Prosser,
J. S., Finnon, P. and Moquest, J. E. (1988): In vitro induction of chromosomal
aberrations in human lymphocytes, with and without boron 10, by radiations
concerned in boron neutron capture therapy. Br. J. Radiol., 61:1136-1141.
(H2) Edwards, A.
A., Lloyd, D. C. and Prosser, J. S. (1990): The induction of chromosome
aberrations in human lymphocytes by 24 keV neutrons. Radiat. Protect. Dosimet.,
31:265-268.
(H3) Aghamohammadi,
S. Z., Goodhead, D. T. and Savage, J. R. K. (1989): Production of chromosome
aberrations, micronuclei, and sister-chromatid exchanges by 24-keV epithermal
neutrons in human G0 lymphocytes. Mutation Res., 211, 225-230.
(H4) Lloyd, D.
C., Purrott, R. J., Dolphin, G. W. and Edwards, A. A. (1976): Chromosome
aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by neutron irradiation. Int. J.
Radiat. Biol., 29:169-182.
(H5) Lloyd, D. C., Purrott, R. J., Reeder,
E. J., et al. (1978): Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes
by radiation from 252Cf. Int. J.
Radiat. Biol., 34:177-186.
(H6) Lloyd, D. C., Edwards, A. A., Prosser, J. S., et al.. (1984): Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by D-T neutrons. Radiat. Res., 98:561-572.
(O1) Dobson, R. L., Straume, T., Carrano,
A. V., Minkler, J. L., Deaven, L. L., Littlefield, L. G. and Awa, A. A.
(1991): Biological effectiveness of neutrons from Hiroshima bomb replica:
Results of a collaborative cytogenetic study. Radiat. Res., 128:143-149.
(O2) Vulpis, N.,
Tognacci, L. and Scorpa, G.. (1978): Chromosome aberrations as a dosimetric
technique for fission neutrons over the dose-range 0.2-50 rad. Int. J. Radiat.
Biol., 33: 301-306.
(O3) Fabry, L., Leonard, A. and Wambersie, A. (1985): Induction of chromosome aberrations in G0
human lymphocytes by low doses of ionizing radiations of different quality.
Radiat. Res., 103:122-134.