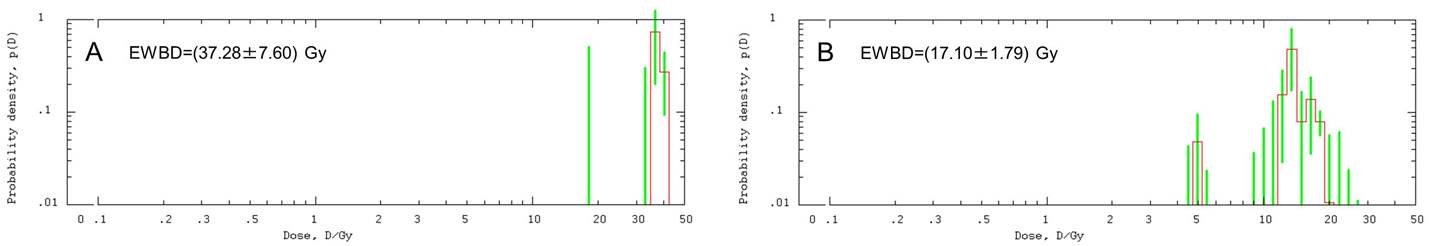
|
Three min after exposure, worker A felt
scorching on his face, stomach-ache and weakness, and developed nausea,
vomiting. Ten min after exposure, worker B suffered from headache, stomach-ache
and started to vomiting.
Two hours later, Both workers were sent to
local hospital. Worker A had the symptom of lethargy, dysphoria, flash on face
and two hands, pressing pain of parotid and abdomen. Temperature was 39.4 oC.
Worker B had diarrhea, congested overlowing on his head and neck. Temperature
was 38 oC.
Both workers were transferred to Hospital
in Beijing 55 hour after the accident. Absolute number of lymphocyte counts
were 0.1×109/L and 0.117×109/L in worker A and B, respectively. The blood samples were obtained from
the workers for chromosome aberration analysis.
| . |
Cellularity in bone marrow at 3 days after the accident |
|
|
Subject |
Neutrophilic stab cells |
Neutrophilic |
Neutrophilic |
Polychromatic |
Orthochromatic |
Lymphocytes |
Monocytes |
Plasma cells |
Reticular cells |
|
|
|
and segmented cells |
myelocytes |
metamyelocytes |
normoblasts |
normoblasts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
95.0 % |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.5 % |
2.5 % |
0 |
1.0 % |
1.0 % |
|
|
B |
85.5 % |
2.5 % |
2.5 % |
0.5 % |
0 |
0 |
0.5 % |
1.5 % |
0 |
. |
Both workers received peripheral blood
stem cells transplantation, but worker A died 33 days after the accident and
worker B died 75 days after.
|
|
Yao, B., Jiang, R., Ai, H. S., Li, Y. F.,
Liu, G. X. and Qiu, L. J. (2010): Biological dose estimation for two severely
exposed patients in a radiation accident in Shandon Jining, China, in 2004.
Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 86:800-808.
|