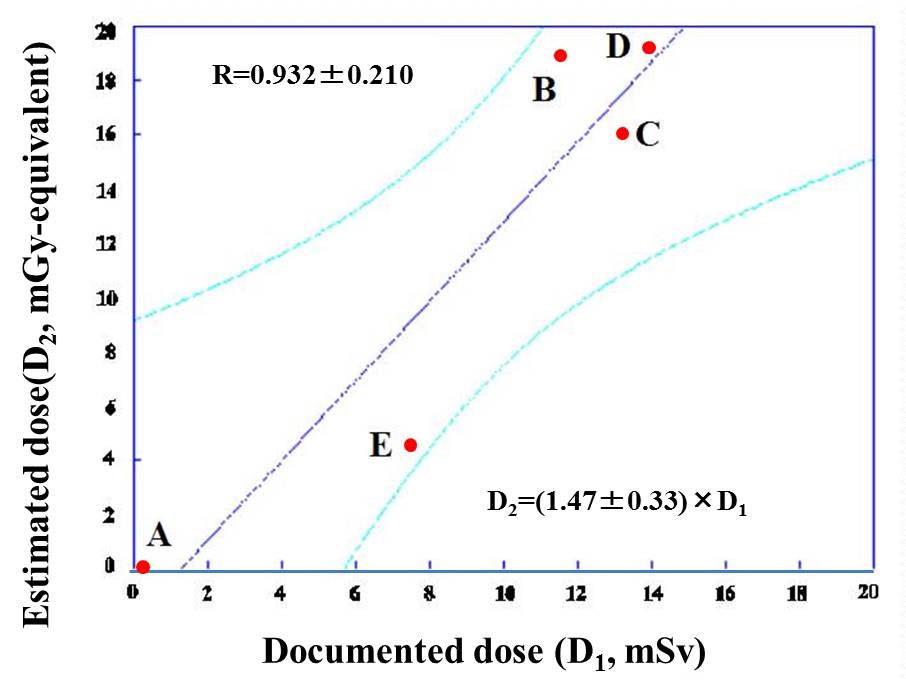
|
JCO emergency actions Criticality accident occurred at 10:35 a.m. of September 30, 1999. Because
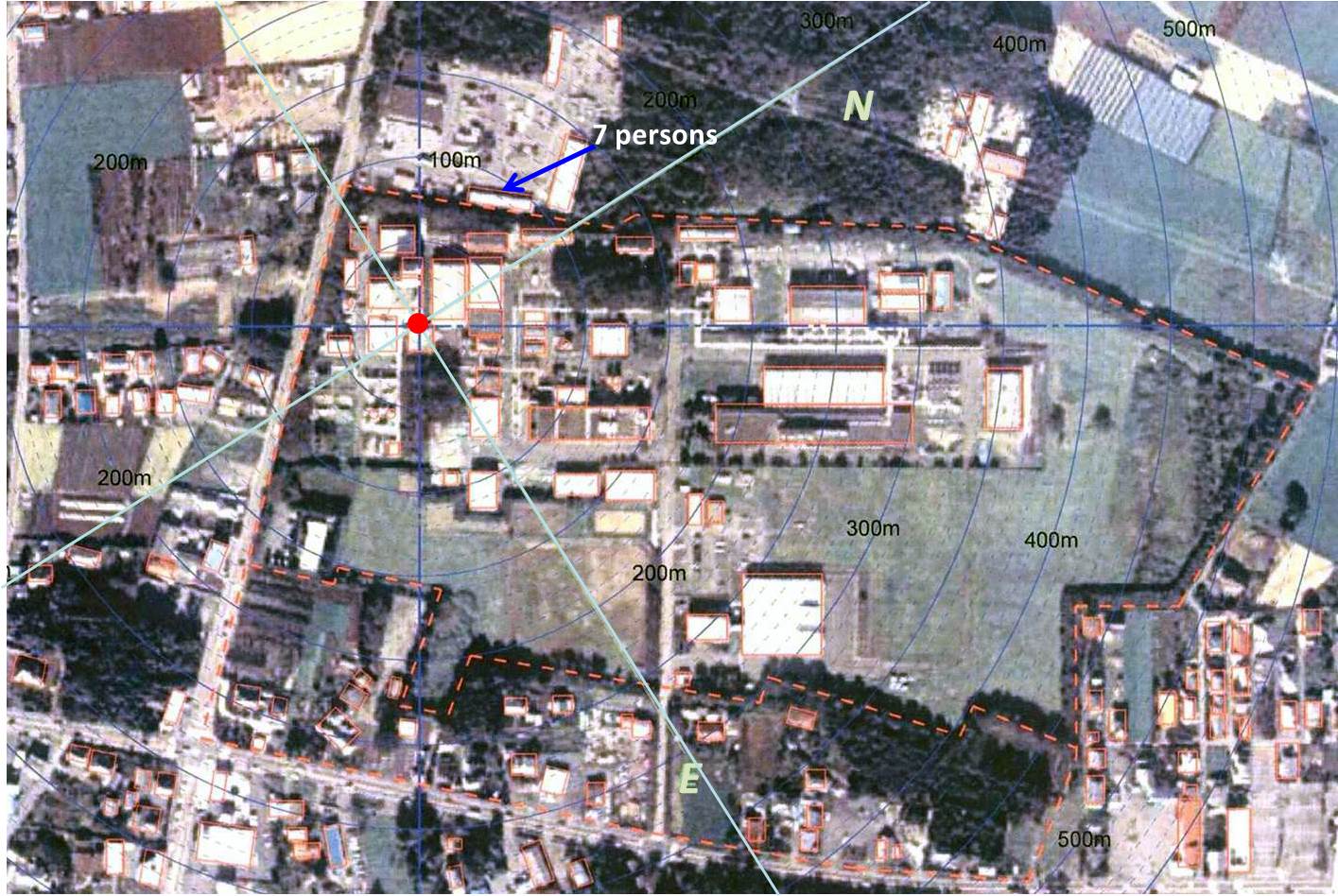
the gamma-ray monitors in the JCO site remained high level, residents (about
200 residents) were recommended to evacuate from the area within 350 m
radius of the conversion facility at 3:00 p.m. The residents within 10
km were recommended to remain in their houses at 10:30. By draining of
cooling water from the cooling jacket of the precipitation tank and injection
of boric acid solution into precipitation tank made the reaction to the
end. Persons involved in the recovery action and rescue task, other emergency
personnel, JCO employees, residents, and their estimated exposure levels
have been reported by S. Tanaka (2001). The cytogenetic survey was carried
out for those persons who agreed to the informed consent. In addition,
lymphocyte chromosomes were also studied in remote residents who showed
severely suppressed lymphocyte counts in the hematological examinations
carried out on October 2-4, 1999 for residents (M. S. Sasaki et al. 2001). Refs: Tanaka, S. (2001): Summary of
the JCO criticality accident in Tokai-mura and dose assessment. J. Radiat.
Res., 42(Suppl): S1-S9. Sasaki, M. S., Hayata, I.,
Kamada, N., Kodama, Y. and Kodama, S. (2001): Chromosome aberration analysis in
persons exposed to low-level radiation from the JCO criticality accident in
Tokai-mura. J. Radiat. Res., 42(Suppl):S107-S116. |
 |